A strategic turn in monetary policy
The BOJ's decision to raise the target overnight call rate to 0.25 % from 0.1 % represents a clear departure from its long-standing policy of combating deflation and stagnant growth through ultra-low interest rates and large-scale bond purchases. This rate hike, the largest since 2007, represents a bold move by BOJ Governor Kazuo Ueda, who has moved away from the unconventional approaches of his predecessor and towards a more traditional monetary framework.
This move by the central bank is particularly noteworthy as it contrasts sharply with the current global trend of lowering interest rates amid economic uncertainty. This divergence is largely due to the BOJ's focus on managing domestic economic pressures, including rising inflation expectations and the potential overheating of some economic sectors.
Yen's reaction
In terms of technical analysis of the Yen, the positive reaction to the interest rate hike came in the wake of the start of the bullish move in mid-July. The closing of yesterday's daily candle saw the external bearish structure break out, which only tentatively signals renewed strength in the Yen. For this idea to be confirmed, it will be necessary for any bearish pullback to take place in a corrective manner, avoiding an impulsive breakdown to new lows.
Price development of the Yen index on the daily time frame
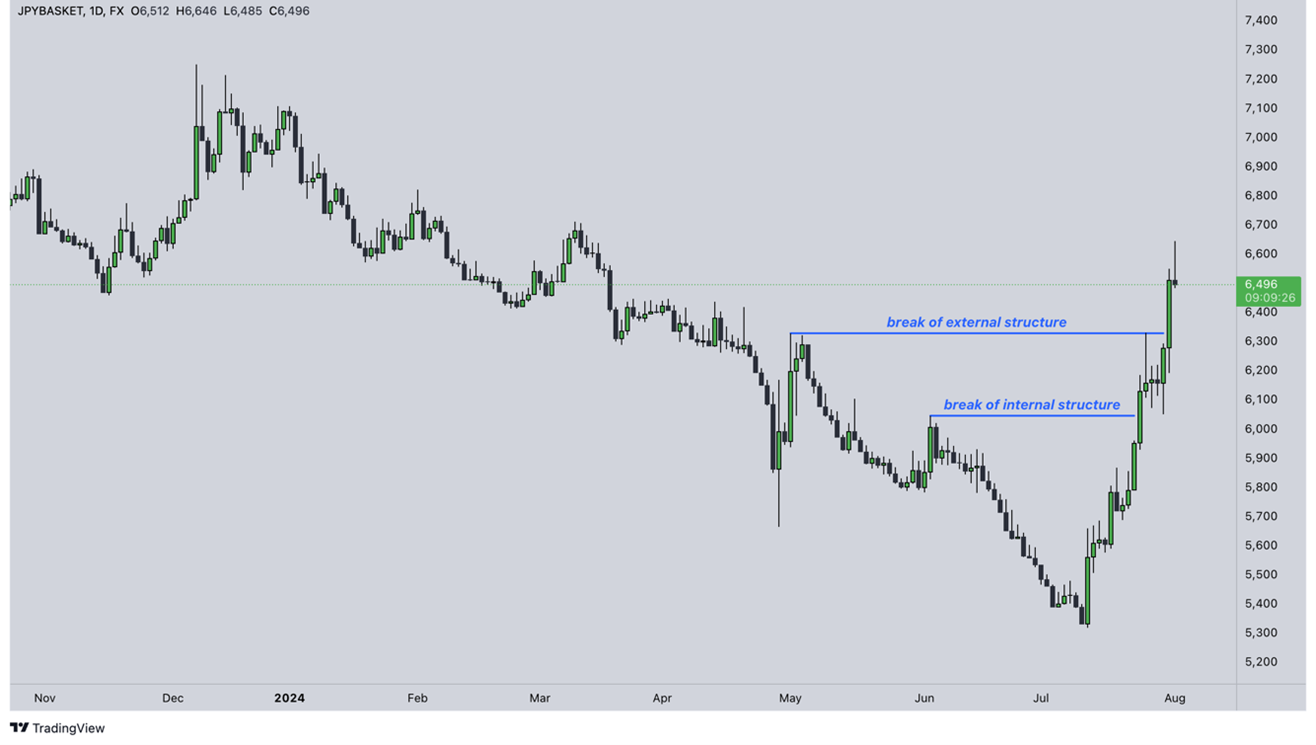
Source: Tradingview
Future rate adjustments and market implications
In his remarks, Governor Ueda hinted at the possibility of further rate hikes later this year, suggesting that the BOJ is prepared to aggressively adjust its policy to achieve a neutral stance that does not stimulate or constrain economic growth. This readiness to continue raising borrowing costs underscores the central bank's determination to stabilize the economy in a prudent and gradual manner, thereby minimizing the risk of sudden financial corrections.
Quantitative tightening and stability
Moreover, the BOJ's plan to curtail its bond-buying program from 2026 onwards signals a strategic approach to quantitative tightening that aims to reduce its balance sheet while mitigating potential disruptions in the bond market. Such a methodical reduction in bond purchases is crucial given that the central bank holds a significant amount of Japanese government bonds, which represent a substantial portion of the market.
Summary
In conclusion, the BOJ's recent policy shift represents both a significant transformation in Japan's economic strategy and a precedent for how central banks might manage the complex interplay of supporting growth while controlling inflation in a volatile global economic environment. The coming months will be crucial in assessing the effectiveness of these measures and their long-term impact on both the Japanese and the global economy.







.jpg)
