Maintenance of Interest Rates
With this decision by the Federal Reserve System, interest rates have remained at the same level since July 2022, in the range of 5.25% to 5.50%. This move was practically expected, but it still resulted in a strengthening of the dollar against the euro, and especially against the Japanese yen, which reached its weakest level in 34 years.
At the same time, the markets expect only one interest rate cut of 0.25% during this year, compared to the six expected cuts at the beginning of the year, with the first potentially occurring as early as this summer.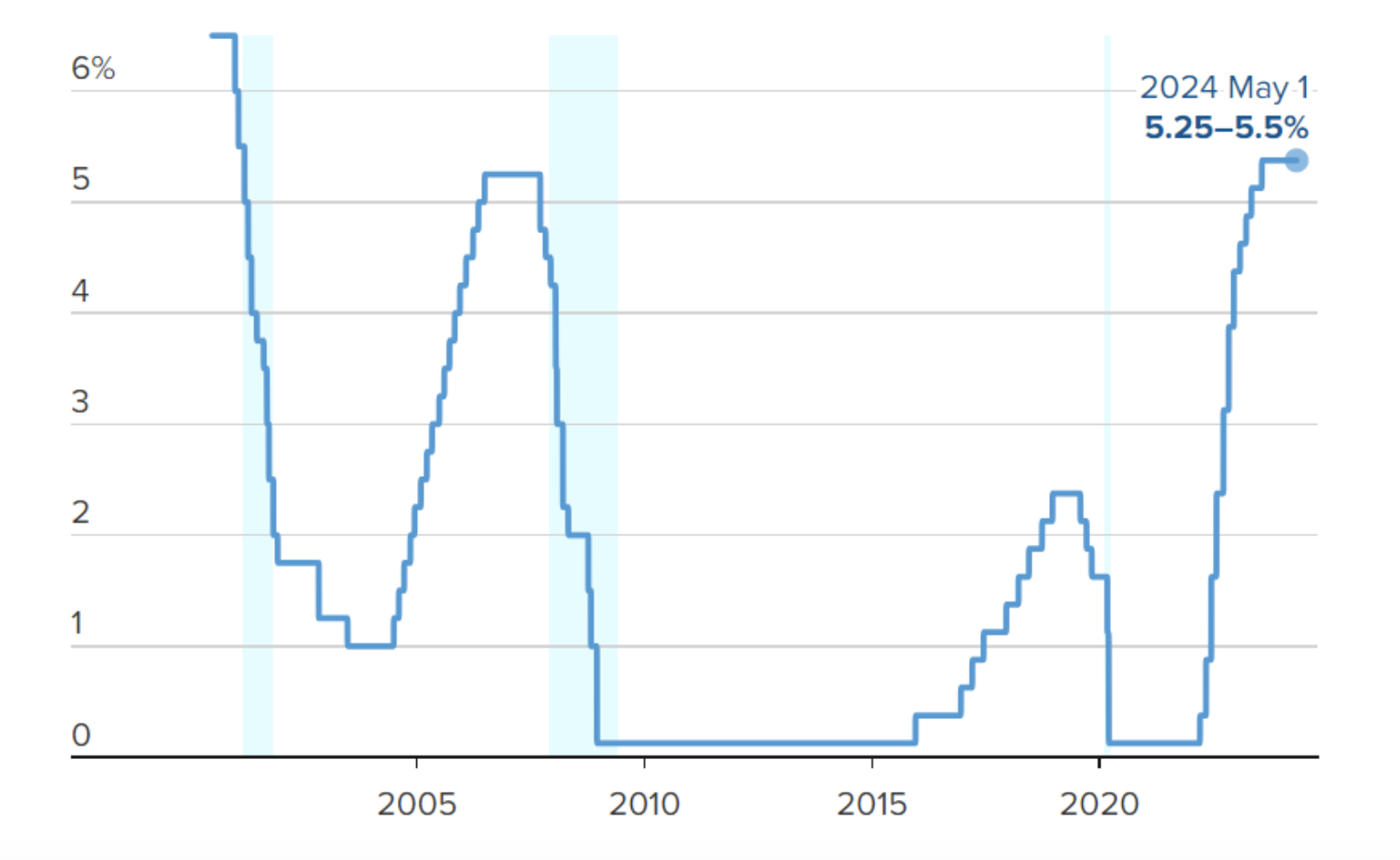
Source: https://www.cnbc.com/2024/05/01/fed-rate-decision-may-2024-.html
Powell's Speech
Following the announcement of the interest rate decision, Jerome Powell gave a speech. In his speech, the Fed chairman emphasized three key points. First was calming the markets by stating that the American central bank does not expect an interest rate hike, although it is not entirely ruled out given the possible development of targeted inflation.
The second point was a declaration emphasizing the Fed's position to decide on interest rates directly at meetings and rejecting a policy of monetary policy decision-making in advance. This is based on the latest data, which, given the current stage of inflation development, can be considered rational.
The third point was the continuation of quantitative tightening. Quantitative tightening is the term used to describe the current reduction of the Fed's balance sheet, which has decreased by $1.5 trillion (1500 billion) from its peak in mid-2022 to $7.5 trillion.
Mechanism of Balance Sheet Reduction
The main mechanism is to let the purchased bonds mature and only buy a small amount of new ones. This way, after the bonds mature, they are removed from the Fed's balance sheet, and by reducing financing, the American economy is cooled, or rather not overheated.
In the case of quantitative easing, the central bank's goal is to purchase a larger volume of bonds than those maturing. During quantitative tightening, the Fed purchased only $60 billion in new Treasury securities and $25 billion in mortgage-backed securities monthly. Now, the volume of newly purchased Treasury securities will decrease to $25 billion per month.
Macroeconomic Context
Although prices continue to rise, it is significantly less than during its peak in mid-2022. Most data in 2024 so far suggests that inflation is well above the Fed's 2% target. The central bank's main indicator shows inflation at 2.7% annually; 2.8% when excluding food and energy in core inflation, on which the Fed focuses specifically as a signal of long-term trends.
At the same time, gross domestic product grew in the first quarter at a lower-than-expected annual rate of 1.6%, raising concerns about potential stagflation with high inflation and slow growth.
The latest Employment Cost Index from the Labor Department this week recorded its largest quarterly increase in a year, sending another negative signal to financial markets out of concern for future interest rate cuts.
Sources:
https://www.cnbc.com/2024/05/01/fed-rate-decision-may-2024-.html



-(1).jpg)



.jpg)
